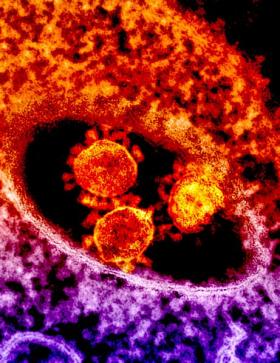
Since causing major outbreaks in Saudi Arabia in 2014, and in Korea a year later, the virus that causes Middle East Respiratory Syndrome is laying low. But by no means has it disappeared: A recent cluster of 34 cases cropped up in July in Riyadh City, Saudi Arabia’s capital. The dromedary camels who harbored the virus for more than 20 years aren’t going anywhere, and neither is MERS.
articles
Alaska's North Slope Snow-Free Season is Lengthening
On the North Slope of Alaska, snow is melting earlier in the spring and the snow-in date is happening later in the fall, according to a new study by CIRES and NOAA researchers. Atmospheric dynamics and sea ice conditions are behind this lengthening of the snow-free season, the scientists found, and the consequences are far reaching—including birds laying eggs sooner and iced-over rivers flowing earlier.
“The timing of snowmelt and length of the snow-free season significantly impacts weather, the permafrost, and wildlife—in short, the Arctic terrestrial system as a whole,” said Christopher Cox, a scientist with CIRES at the University of Colorado Boulder and NOAA’s Physical Sciences Division in Boulder, Colorado. The study has been accepted for publication in the Bulletin of the American Meteorological Society.
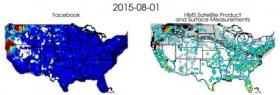
Where there's fire, there's smoke – and social media
When people see smoke on the horizon, what do they do? Besides (hopefully) calling fire authorities, they post to social media, of course.
The fact that people reliably flock to social media to discuss smoke and fire was the inspiration for a new study by Colorado State University atmospheric scientists. Driven to innovate ways to improve the air we breathe, the scientists have shown that social media, Facebook in this case, could prove a powerful tool.
Isotope fingerprints in feathers reveal songbirds' secret breeding grounds
Using isotope fingerprints in feathers, researchers have pinpointed the northern breeding grounds of a small, colourful songbird.
Myrtle warblers breed across much of Canada and the eastern United States, but winter in two distinct groups—one along the Atlantic and Gulf coasts, another along the US Pacific Coast. They are also one of the few breeds of eastern warbler that have been able to extend their range into the far northwest of the continent.
NASA's Voyager Spacecraft Still Reaching for the Stars
Humanity's farthest and longest-lived spacecraft, Voyager 1 and 2, achieve 40 years of operation and exploration this August and September. Despite their vast distance, they continue to communicate with NASA daily, still probing the final frontier. Their story has not only impacted generations of current and future scientists and engineers, but also Earth's culture, including film, art, and music. Each spacecraft carries a Golden Record of Earth sounds, pictures, and messages. Since the spacecraft could last billions of years, these circular time capsules could one day be the only traces of human civilization.
"None of us knew, when we launched 40 years ago, that anything would still be working, and continuing on this pioneering journey," said Ed Stone, Voyager project scientist at Caltech in Pasadena, California. "The most exciting thing they find in the next five years is likely to be something that we didn't know was out there to be discovered."
Tropical Depression 11E ''Born'' With Wind Shear on Satellite Imagery
The eleventh tropical depression of the Eastern Pacific Ocean hurricane season came together on August 4 even though it was being affected by vertical wind shear.
NOAA's GOES-West satellite captured a visible image of Tropical Depression 11E on August 4, 2017 at 10:45 a.m. EDT (1445 UTC) in the Eastern Pacific Ocean. The image showed that the bulk of clouds appeared on the western side of the storm, which indicates wind shear was likely affecting the storm.