A new type of smart fabric developed at the University of Washington could pave the way for jackets that store invisible passcodes and open the door to your apartment or office.
articles
Antarctic Research Station To Close As Cracks In Ice Shelf Grow
A research station in Antarctica, the Halley VI, will be temporarily shut down for the second year in a row among concerns over deep, growing cracks in the ice shelf on either side of the facility, The Guardian reported. The station, which sits atop the nearly 500-foot thick Brunt ice shelf, is operated by the British Antarctic Survey (BAS).
Every day is Halloween for these eerie insects
With Halloween upon us, it’s worth remembering that living things take part in similar costume parties all year long, adopting weird and wonderful forms.
Though rather than a haul of candy, organisms might earn the chance to live, prosper and mate. It’s all part of evolution, the principle where the fittest individuals pass their genes onto the next generation.
FUTURE VOLCANIC ERUPTIONS COULD CAUSE MORE CLIMATE DISRUPTION
Major volcanic eruptions in the future have the potential to affect global temperatures and precipitation more dramatically than in the past because of climate change, according to a new study led by the National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR).
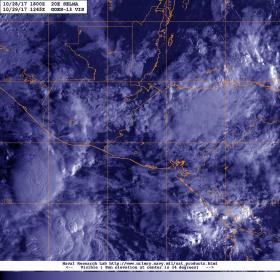
Satellite Shows Post-tropical Cyclone Selma Dissipate
NOAA's GOES East satellite provided an image of Post-Tropical Cyclone Selma as it dissipated near the border of El Salvador and Honduras.
Technologies shine spotlight on climate role of undersea canyons
Unprecedented high-resolution data from undersea canyons off Vancouver Island’s west coast is bringing new understanding of the importance of these canyons as rapid-transit corridors for carrying carbon from the ocean surface to the deep sea.
An international study co-led by Ocean Networks Canada (ONC) staff scientist and University of Victoria biologist Fabio De Leo uses synchronized real-time data from “Wally” the deep-sea crawler and NASA’s MODIS satellite for the first time to measure carbon transport from the sea surface to the deep ocean by wintertime ocean circulation, canyon rim eddies and downwelling – the sinking of dense, cold water beneath lighter, warmer water.