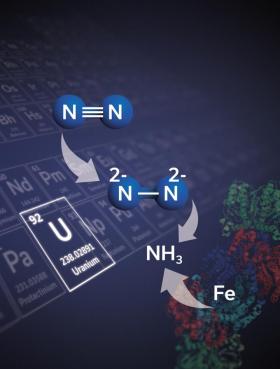
Small farmers and indigenous communities have practised sustainable agriculture for centuries. Chidi Oguamanam is working to ensure that traditional knowledge is recognized and shared equitably.
The kind of clean technology Chidi Oguamanam advocates looks a lot different from what many of us might imagine. No high-tech solar panels. No futuristic gizmos. No scientists in a lab.