Enfrentando una crisis climática, algún día podemos rociar dióxido de azufre en la atmósfera superior para formar una nube que enfría la Tierra, pero suspender repentinamente esta fumigación tendría un impacto global severo en animales y plantas, según el primer estudio sobre los impactos biológicos potenciales. de geoingeniería o intervención climática.
articles
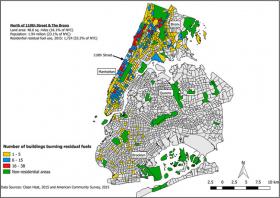
Use of Dirty Heating Oil in NYC Concentrated Uptown
Residential buildings in New York City that burn residual fuel oil were concentrated in Northern Manhattan and the Bronx, as of late 2015. Compared to cleaner heating sources such as natural gas, these dirty fuels produce high levels of particulate matter, exposure to which is linked to asthma, obesity, developmental delays, and other health problems.
Small hydroelectric dams increase globally with little research, regulations
Hydropower dams may conjure images of the massive Grand Coulee Dam in Washington state or the Three Gorges Dam in Hubei, China — the world’s largest electricity-generating facility. But not all dams are the stuff of documentaries. Tens of thousands of smaller hydroelectric dams exist around the world, and all indications suggest that the number could substantially increase in the future.
Researchers reveal how microbes cope in phosphorus-deficient tropical soil
A team led by the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory has uncovered how certain soil microbes cope in a phosphorus-poor environment to survive in a tropical ecosystem. Their novel approach could be applied in other ecosystems to study various nutrient limitations and inform agriculture and terrestrial biosphere modeling.
Seabed mining could destroy ecosystems
Mining on the ocean floor could do irreversible damage to deep-sea ecosystems, says a new study of seabed mining proposals around the world.
Wild Sri Lankan elephants retreat from sound of Asian honey bees
Playbacks have been used for many years to explore the behavioural responses of African elephants to a suspected natural threat. However, the research published in Current Biology, is the first time this technique has been used to record how Asian elephants react to the sound of bees.
The study, led by Dr Lucy King, a Research Associate with the Department of Zoology at Oxford University and head of the Human-Elephant Co-Existence Program for Save the Elephants, showed that Asian elephants responded with alarm to the bee simulations. They also retreated significantly further away and vocalised more in response to the bee sounds compared to controls.