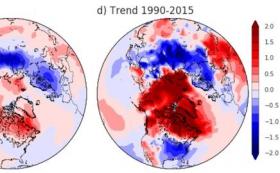
When the strong winds that circle the Arctic slacken, cold polar air can escape and cause extreme winter chills in parts of the Northern hemisphere.
articles
UMN researchers find recipe for forest restoration
To find out what works best for reestablishing tropical dry forests, the researchers planted seedlings of 32 native tree species in degraded soil or degraded soil amended with sand, rice hulls, rice hull ash or hydrogel.
We must accelerate transitions for sustainability and climate change, experts say
We must move faster towards a low-carbon world if we are to limit global warming to 2 degrees C this century, experts have warned.
Crowning the "King of the Crops": Sequencing the White Guinea Yam Genome
An international collaboration involving the Earlham Institute, Norwich, UK, and the Iwate Biotechnology Research Centre, Japan, has for the first time provided a genome sequence for the white Guinea yam, a staple crop with huge economic and cultural significance on the African continent and a lifeline for millions of people.
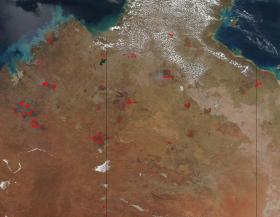
Fires in Australia Pop Up in Places Already Burned
Fires that span across the Northern Territory and Western Australia appear to have broken out in areas that have already been burned in previous fires. Areas that sport "burn scars", those areas that are a darker, almost red-brown color, are surrounded by fires that are anywhere from a few hours old to 7 days old. The areas that are seven days old can be attributed to fires that spread but areas that are just a few hours old may be fires that have presumably been put out only to have them break out again. The Northern Territory of Australia experienced a higher than normal amount of rain this past season allowing the plants and trees that fuel fires to become even more overgrown and subject to becoming fire fodder.
NASA Tracking Hurricane Maria on Bahamas Approach
NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite provided a look at Maria's temperatures to find the strongest sides of the storm, while NOAA's GOES satellite revealed the extent of the storm in a visible image as it moved toward the Bahamas.