New research from North Carolina State University finds that urban warming reduces growth and photosynthesis in city trees. The researchers found that insect pests are part of the problem, but that heat itself plays a more significant role.
articles
Non-toxic solvent removes barrier to commercialisation of perovskite solar cells
Scientists at Oxford University have developed a solvent system with reduced toxicity that can be used in the manufacture of perovskite solar cells, clearing one of the barriers to the commercialisation of a technology that promises to revolutionise the solar industry.
Perovskites – a family of materials with the crystal structure of calcium titanate – have been described as a 'wonder material' and shown to be almost as efficient as silicon in harnessing solar energy, as well as being significantly cheaper to produce.
New Technology Helps Pinpoint Sources of Water Contamination
Berkeley Lab develops better method of environmental monitoring using the PhyloChip, finds surprising results in Russian River watershed
When the local water management agency closes your favorite beach due to unhealthy water quality, how reliable are the tests they base their decisions on? As it turns out, those tests, as well as the standards behind them, have not been updated in decades. Now scientists from Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (Berkeley Lab) have developed a highly accurate, DNA-based method to detect and distinguish sources of microbial contamination in water.
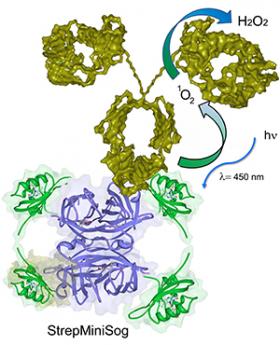
UC Researcher Develops Clean Water-Treatment Option to Target Sporadic Outbreaks
A University of Cincinnati scientist has engineered an environmentally friendly technology to zap outbreak-causing viruses and bacteria from public drinking water.
Environmental and biomedical engineer David Wendell, an associate professor in UC’s College of Engineering and Applied Science, developed a protein-based photocatalyst that uses light to generate hydrogen peroxide to eliminate E. coli, Listeria, and potentially protozoa like giardia and cryptosporidium.
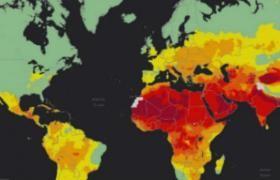
El 92% de la población mundial expuesta a niveles peligrosos de contaminación del aire
Un nuevo modelo de calidad del aire de la OMS confirma que el 92% de la población mundial vive en lugares donde los niveles de calidad del aire exceden límites establecidos por la misma OMS. La información se presenta a través de mapas interactivos, destacando las áreas dentro de los países que exceden los límites de la OMS.
The Psychology Behind Climate Change Denial
Climate change is a serious threat to humans, animals, and the earth’s ecosystems. Nevertheless, effective climate action has been delayed, partly because some still deny that there is a problem. In a new thesis in psychology, Kirsti Jylhä at Uppsala University has studied the psychology behind climate change denial. The results show that individuals who accept hierarchical power structures tend to a larger extent deny the problem.
In the scientific community there is a strong consensus that humans have significantly affected the climate and that we are facing serious challenges. But there is a lot of misinformation about climate change in circulation, which to a large part is created and distributed by organised campaigns with the aim of postponing measures that could combat climate change. And there are people who are more prone than others to trust this misinformation.
Previous research has consistently shown that it is more common among politically conservative individuals to deny climate change. In her thesis, Kirsti Jylhä has investigated this further and in more detail. Her studies included ideological and personality variables which correlate with political ideology, and tested if those variables also correlate with climate change denial.