Effects of livestock grazing on greater sage-grouse populations can be positive or negative depending on the amount of grazing and when grazing occurs, according to research published today in Ecological Applications. The research was conducted by scientists from the United States Geological Survey, Colorado State University and Utah State University.
articles
"Geofencing" Shows Promise in Tracking Chronic Care
Location-tracking apps on smartphones could be used to help track and manage care for thousands of patients who suffer from chronic diseases, and possibly even provide feedback to them on lifestyle changes that could help, according to an initial assessment by researchers at UC San Francisco.
In the study, researchers provided a smartphone app to 3,443 participants age 18 and older from all 50 states. The app, which was developed by app developer Ginger.io in collaboration with study investigators, used “geofencing,” a location-based program that defines geographical boundaries. This app tracked participants when they entered a hospital and triggered a questionnaire when they were located in the hospital for more than four hours.
Futuristic Clock Prepared for Space
No one keeps time quite like NASA.
Last month, the space agency's next-generation atomic clock was joined to the spacecraft that will take it into orbit in late 2017.
That instrument, the Deep Space Atomic Clock was developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. On Feb. 17, JPL engineers monitored integration of the clock on to the Surrey Orbital Test Bed spacecraft at Surrey Satellite Technology in Englewood, Colorado.
The foundation of aquatic life can rapidly adapt to global warming, new research suggests
Important microscopic creatures which produce half of the oxygen in the atmosphere can rapidly adapt to global warming, new research suggests.
Phytoplankton, which also act as an essential food supply for fish, can increase the rate at which they take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen while in warmer water temperatures, a long-running experiment shows.
Monitoring of one species, a green algae, Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, after ten years of them being in waters of a higher temperature shows they quickly adapt so they are still able to photosynthesise more than they respire.
A new, gel-like coating beefs up the performance of lithium-sulfur batteries
Yale scientists have developed an ultra-thin coating material that has the potential to extend the life and improve the efficiency of lithium-sulfur batteries, one of the most promising areas of energy research today.
In a study published online March 20 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, researchers describe the new material — a dendrimer-graphene oxide composite film — which can be applied to any sulfur cathode. A cathode is the positive terminal on a battery.
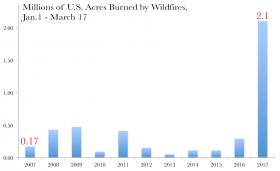
2017 U.S. Wildfire Season Off to an Intense Start
Wildfires have consumed more than 2 million acres of U.S. land so far this year, nearly 10 times the long-term average and a punishing start to this year’s wildfire season, according to data from the National Interagency Fire Center (NIFC).