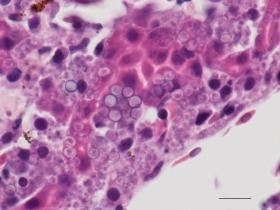
A deadly amphibian disease called severe Perkinsea infections, or SPI, is the cause of many large-scale frog die-offs in the United States, according to a new study by the U.S. Geological Survey.
Frogs and salamanders are currently among the most threatened groups of animals on the planet. The two most common frog diseases, chytridiomycosis and ranavirus infection, are linked to frog population declines worldwide. The new study suggests that that SPI is the third most common infectious disease of frogs.