Mercury is one of the top 10 chemical concerns for public health according to the World Health Organization (WHO). In more than half of Swedish lakes the mercury levels are so high that eating the fish is a threat to the health of people and wildlife. To make matters worse, the problem seems to have no solution in sight. But new research gives hope: the mercury problem could very well be blowing away in the wind.
articles
New Technique Can Detect Impurities in Ground Beef Within Minutes
Researchers at the University of British Columbia have found a better way to identify unwanted animal products in ground beef.
UBC Study Finds Family-Friendly Overpasses are Needed to Help Grizzly Bears
Researchers have determined how female grizzly bears keep their cubs safe while crossing the Trans-Canada Highway.
Floods Are Necessary for Maintaining Healthy River Ecosystems
Flooding rivers can wreak havoc on homes and roads but are necessary for healthy ecosystems, research at Oregon State University suggests.
When Friends Become Objects
Why do people use social media? Striving to answer this question, social psychologists at Ruhr-Universität Bochum (RUB) have conducted a survey with more than 500 Facebook users with regard to their personality structure and the way they use the platform. Based on the results, they have developed the first comprehensive theory of social media usage. According to that theory, self-regulation is the key: we use Facebook in a way that makes us feel good and hope to attain our objectives. The research team manned by Phillip Ozimek, Fiona Baer and Prof Dr Jens Förster published their report in the journal Heliyon on November 20, 2017.
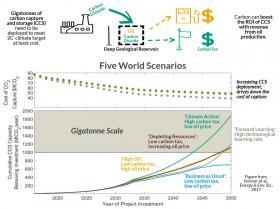
Carbon Capture is Helped by Oil Revenue, But it May Not Be Enough
The oil industry incentivises the development of carbon-capturing tech, but researchers say this will not reduce emissions to low enough levels.