Using a modified version of the CRISPR genome-editing system, MIT researchers have developed a new way to screen for genes that protect against specific diseases.
articles
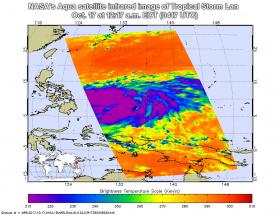
NASA Finds Tropical Storm Lan Strengthening
Infrared imagery from NASA's Aqua satellite revealed that Tropical Storm Lan was getting stronger as it moved through the Northwestern Pacific Ocean.
Study reshapes understanding of climate change's impact on early societies
A new study linking paleoclimatology — the reconstruction of past global climates — with historical analysis by researchers at Yale and other institutions shows a link between environmental stress and its impact on the economy, political stability, and war-fighting capacity of ancient Egypt.
The team of researchers examined the hydroclimatic and societal impacts in Egypt of a sequence of tropical and high-latitude volcanic eruptions spanning the past 2,500 years, as known from modern ice-core records. The team focused on the Ptolemaic dynasty of ancient Egypt (305-30 B.C.E.) — a state formed in the aftermath of the campaigns of Alexander the Great, and famed for rulers such as Cleopatra — as well as material and cultural achievements including the great Library and Lighthouse of Alexandria.
Fighting fires before they spark
With warm, dry summers comes a deadly caveat for the western United States: wildfires. Scientists say the hot, dry climates found west of the Mississippi, along with decades of fire suppression efforts, are creating a devastating and destructive combination – leading to fires like the ones currently burning in California.
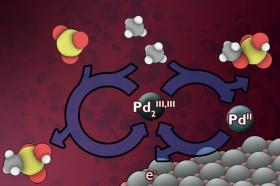
A New Way to Harness Wasted Methane
Methane gas, a vast natural resource, is often disposed of through burning, but new research by scientists at MIT could make it easier to capture this gas for use as fuel or a chemical feedstock.
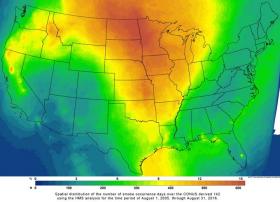
UAH graduate student uncovers link between forest fire smoke, pollution events
Smoke from forest fires might contribute to more than half of certain gritty air pollution events in the continental U.S. during the summer, and as much as 20 percent of those events throughout the year, according to new research at The University of Alabama in Huntsville (UAH).