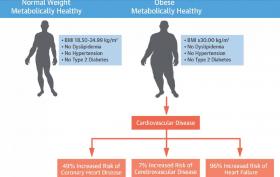
Clinicians are being warned not to ignore the increased cardiovascular health risks of those who are classed as either ‘healthy obese’ or deemed to be ‘normal weight’ but have metabolic abnormalities such as diabetes.
articles
NASA Gets Night-Time and Daytime Look at a Weaker Wide Irma
NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite captured night-time look at Hurricane Irma as it weakened to a large tropical storm and the GOES East satellite provided a daytime view as the large storm continued moving north over Florida.
WHY YOUR ANCESTORS WOULD HAVE ACED THE LONG JUMP
A 52-million-year-old ankle fossil suggests our prehuman ancestors were high-flying acrobats.
These first primates spent most of their time in the trees rather than on the ground, but just how nimble they were as they moved around in the treetops has been a topic of dispute.
For years, scientists thought the ancestors of today’s humans, monkeys, lemurs and apes were relatively slow and deliberate animals, using their grasping hands and feet to creep along small twigs and branches to stalk insects or find flowers and fruits.
Desert locusts: new risks in the light of climate change
Desert locusts are a major pest on numerous crops and pastures throughout a vast area of almost 30 million km2 covering Africa north of the equator, the Near East, the Arabian Peninsula and the Indian subcontinent. Like other locusts, desert locusts can switch from a solitary phase with low population densities during recessions (periods of calm), to a gregarious phase with high population densities during invasions, when hopper bands and swarms can devastate agriculture.
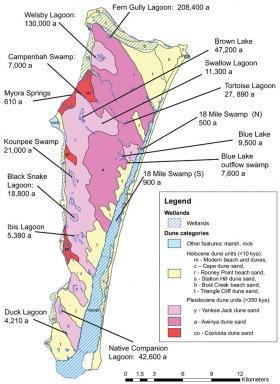
Ancient wetlands offer window into climate change
The work – led by the University of Adelaide, and involving scientists from the Queensland Government, and members of the local community – has uncovered what the researchers describe as a "treasure trove" of ancient wetlands on Queensland's North Stradbroke Island (known to Indigenous communities as Minjerribah), some dating as old as 200,000 years ago.
Air pollution cuts three years off lifespans in northern China
There are currently an estimated 4.5 billion people around the world exposed to levels of particulate air pollution that are at least twice what the World Health Organization considers safe. Yet the impact of sustained exposure to pollution on a person’s life expectancy has largely remained a vexingly unanswered question—until now.