
Perovskite solar cells are an alternative to conventional silicon solar cells, and are poised to overtake the market with their high power-conversion efficiencies (over 22% now) and lower capital expenditure and manufacturing costs. But one of the greatest obstacles on this road is stability: to be commercially viable, perovskite solar cells must also be able to maintain their efficiency over time, meaning that they must not degrade significantly over 25 years of service.
>> Read the Full Article

It is well understood how flowers use complex color patterns and smells to attract pollinating bees. But now, scientists have discovered that flowers also emit heat to advertise themselves to insects — creating temperature arrays that mimic the color designs of petals.
On average, heat spots were 4 to 5 degrees Celsius warmer than the rest of the flower, but could be as much as 11 degrees warmer.
>> Read the Full Article

Scientists at Michigan State University have shown that streams can be key health indicators of a region’s landscape, but the way they’re being monitored can be improved.
New research featured in Ecology Letters showcases how streams can be used as sensors to diagnose a watershed’s sensitivity or resiliency to changes in land use practices, including the long-term use of fertilizers. Using streams as sensors – specifically, near the headwaters – can allow scientists, land-use managers and farmers to diagnose which watersheds can be more sustainably developed for food production, said Jay Zarnetske, MSU earth and environmental scientist and co-author of the study.
>> Read the Full Article
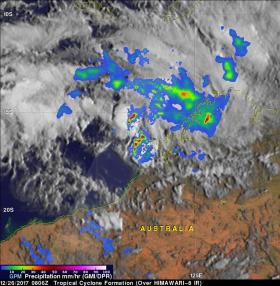
As Tropical Cyclone Hilda was coming together in the Southern Indian Ocean the GPM satellite analyzed its rainfall from space.
On December 26, 2017 at 3:06 a.m. EST (0806 UTC) the Global Precipitation Measurement mission or GPM core observatory satellite flew above northwestern Australia and measured rainfall as Tropical Cyclone Hilda was forming along the coast
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment