
Logging that happens today and potential future rainfall reductions in the Amazon could push the region into a vicious dieback circle. If dry seasons intensify with human-caused climate change, the risk for self-amplified forest loss would increase even more, an international team of scientists finds. If however there is a great variety of tree species in a forest patch, according to the study this can significantly strengthen the chance of survival. To detect such non-linear behavior, the researchers apply a novel complex network analysis of water fluxes.
“The Amazon rainforest is one of the tipping elements in the Earth system,” says lead-author Delphine Clara Zemp who conducted the study at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, Germany. “We already know that on the one hand, reduced rainfall increases the risk of forest dieback, and on the other hand, forest loss can intensify regional droughts. So more droughts can lead to less forest leading to more droughts and so on. Yet the consequences of this feedback between the plants on the ground and the atmosphere above them so far was not clear. Our study provides new insight into this issue, highlighting the risk of self-amplifying forest loss which comes on top of the forest loss directly caused by the rainfall reduction.” This study results from the German-Brazilian Research Training Group on Dynamical Phenomena in Complex Networks at (IRTG1740) hosted by Humboldt Universität zu Berlin.
>> Read the Full Article

Accurately predicting the weather - at short and long time scales - is among the most complex and important challenges faced by science. Protecting the nation’s security and economic well-being will increasingly rely on improved skill in forecasting weather, weather-driven events like floods and droughts, and long-term shifts in weather, ocean and sea-ice patterns.
>> Read the Full Article

Everyone knows that exercise is good for you, but what type of training helps most, especially when you’re older - say over 65? A Mayo Clinic study says it’s high-intensity aerobic exercise, which can reverse some cellular aspects of aging. The findings appear in Cell Metabolism.
Mayo researchers compared high-intensity interval training, resistance training and combined training. All training types improved lean body mass and insulin sensitivity, but only high-intensity and combined training improved aerobic capacity and mitochondrial function for skeletal muscle. Decline in mitochondrial content and function are common in older adults.
>> Read the Full Article
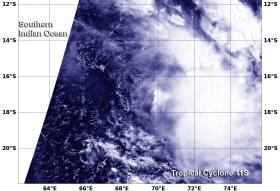
Tropical Cyclone 11S appeared elongated in NASA satellite imagery as a result of the storm being battered by wind shear.
When NASA's Terra satellite flew over Tropical Cyclone 11S on March 10 at 0515 UTC (12:15 a.m. EST) the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument took a visible light picture of the storm. The image revealed that the storm has been stretched out by moderate vertical wind shear.
>> Read the Full Article

There is no mint that can take the edge off sulfurous emissions from volcanoes, but researchers can use remote sensing to better understand volcanic breathing.
Volcanoes erupt, they spew ash, their scarred flanks sometimes run with both lava and landslides. But only occasionally. A less dramatic but important process is continuous gas emissions from volcanoes; in other words, as they exhale. A number of volcanoes around the world continuously exhale water vapor laced with heavy metals, carbon dioxide, hydrogen sulfide and sulfur dioxide, among many other gases. Of these, sulfur dioxide is the easiest to detect from space.
>> Read the Full Article

The 2011 Fukushima catastrophe is an ongoing disaster whose end only gets more remote as time passes. The government is desperate to get evacuees back into their homes for the 2020 Tokyo Olympics, but the problems on the ground, and in the breached reactor vessels, are only getting more serious and costly, as unbelievable volumes of radiation contaminate land, air and ocean.
>> Read the Full Article

With their measurements and samples, nearly 3,500 schoolchildren have assisted a research study on lakes and global warming, now published in an academic journal. The results show that water temperatures generally remain low despite the air becoming warmer. This helps to curb the outflow of greenhouse gases.
>> Read the Full Article

Conservationists working to safeguard tropical forests often assume that old growth forests containing great stores of carbon also hold high biodiversity, but a new study finds that the relationship may not be as strong as once thought, according to a group of researchers with contributions from WCS (Wildlife Conservation Society) and other organizations.
Tropical forests are exceptionally rich in both carbon and biodiversity, but the study recently published in the journal Scientific Reports indicates that, within the tropics, tree diversity and forest carbon do not necessarily correlate, and that there is no detectable relationship between the two factors across a region, a scale relevant for conservation planning and the establishment of protected areas. For instance, in Central Africa, some areas that are dominated by one or a few tree species are high in carbon density, whereas some forests with many more tree species have a lower carbon density.
>> Read the Full Article

Growing sustainable energy crops without increasing greenhouse gas emissions, may be possible on seasonally wet, environmentally sensitive landscapes, according to researchers who conducted a study on Conservation Reserve Program (CRP) land.
Debasish Saha, postdoctoral scholar in plant sciences, Penn State College of Agricultural Sciences, and colleagues measured the amount of nitrous oxide, a potent greenhouse gas, emanating from plots of biofuels-producing switchgrass — a native perennial grass — and miscanthus — a non-native grass species — growing in an experimental area in eastern central Pennsylvania and compared it to emissions from adjacent, undisturbed CRP acres. The experiment took place in a long-term monitoring site managed by the U.S. Department of Agriculture's Agricultural Research Service.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment