
International research team reports ocean acidification spreading rapidly in Arctic Ocean in area and depth
Ocean acidification (OA) is spreading rapidly in the western Arctic Ocean in both area and depth, according to new interdisciplinary research reported in Nature Climate Change by a team of international collaborators, including University of Delaware professor Wei-Jun Cai.
The research shows that, between the 1990s and 2010, acidified waters expanded northward approximately 300 nautical miles from the Chukchi slope off the coast of northwestern Alaska to just below the North Pole. Also, the depth of acidified waters was found to have increased, from approximately 325 feet to over 800 feet (or from 100 to 250 meters).
>> Read the Full Article
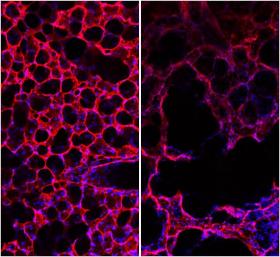
Smoke from cigarettes blocks self-healing processes in the lungs and consequently can lead to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Researchers at the Helmholtz Zentrum München, partner in the German Center for Lung Research (DZL), and their international colleagues have reported this in the American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine.
>> Read the Full Article

Philadelphia communities along the Schuylkill River and Darby Creek now have new tools to help inform residents of impending flooding. The U.S. Geological Survey recently installed three new streamgages in Manayunk, Eastwick, and downtown near 30th St., which will monitor water levels, and provide vital data used by emergency managers and flood forecasters to help protect lives and property.
>> Read the Full Article
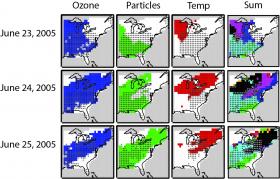
The combination of prolonged hot spells with poor air quality greatly compounds the negative effects of each and can pose a major risk to human health, according to new research from the University of California, Irvine.
“The weather factors that drive heat waves also contribute to intensified surface ozone and air pollution episodes,” said UCI professor of Earth system science Michael J. Prather, co-author of the study, published this week in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. “These extreme, multiday events tend to cluster and overlap, worsening the health impacts beyond the sum of their individual effects.”
>> Read the Full Article

A University of Florida study shows that mollusk fossils provide a reliable measure of human-driven changes in marine ecosystems and shifts in ocean biodiversity across time and space.
Collecting data from the shells of dead mollusks is a low-cost, low-impact way of glimpsing how oceans looked before pollution, habitat loss, acidification and explosive algae growth threatened marine life worldwide. Mollusk fossils can inform current and future conservation and restoration efforts, said Michal Kowalewski, the Jon L. and Beverly A. Thompson Chair of Invertebrate Paleontology at the Florida Museum of Natural History on the UF campus and the study’s principal investigator.
>> Read the Full Article

Researchers in the Singapore-ETH Centre’s Future Cities Laboratory developed a method to quantify ecosystem services of street trees. Using nearly 100,000 images from Google Street View, the study helps further understanding on how green spaces contribute to urban sustainability.
Do you remember the last time you escaped the hot summer sun to enjoy a cool reprieve in the shade beneath a broad-leafed tree? While sizzling summer days may seem far away right now in the northern hemisphere, tropical cities like Singapore deal with solar radiation on a daily basis.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment