
Dining in dimly lit restaurants has been linked to eating slowly and ultimately eating less than in brighter restaurants, but does lighting also impact how healthfully we order?
New research findings forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing Research illustrate that those dining in well-lit rooms are about 16-24% more likely to order healthy foods than those in dimly lit rooms. Furthermore, the researchers found evidence that this effect is due mainly to the level of diners’ alertness. “We feel more alert in brighter rooms and therefore tend to make more healthful, forward-thinking decisions,” explains lead author Dipayan Biswas, PhD, University of South Florida.
>> Read the Full Article

Over fifty percent of the United States energy comes from coal and petroleum based fuels. Powering a nation in which the average person uses the amount of energy in 15,370 lbs of coal or 165,033 sticks of dynamite in a year is not sustainable. When thinking of a solution, the well-known renewable energy source that most likely comes to mind is solar power.
Solar panels are an impervious surface. Impervious surfaces already take up 32,868.61 square miles of roads, parking lots, driveways, and more. These surfaces displace rainwater to surrounding areas and have great impacts on the water table and soil quality. Utilizing already cleared land rather than clearing more would be beneficial to the environment, as solar fields require large amounts of cleared land.
>> Read the Full Article

Unlike the declining populations of many fish species, the number of cephalopods (octopus, cuttlefish and squid) has increased in the world's oceans over the past 60 years, a University of Adelaide study has found.
The international team, led by researchers from the University's Environment Institute, compiled a global database of cephalopod catch rates to investigate long-term trends in abundance, published in Cell Press journal Current Biology.
>> Read the Full Article
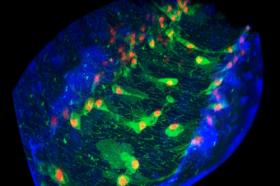
Immune cells play essential roles in the maintenance and repair of our bodies. When we injure ourselves, immune cells mount a rapid inflammatory response to protect us against infection and help heal the damaged tissue.
Lead researcher Dr Helen Weavers, from the Faculty of Biomedical Sciences said: “While this immune response is beneficial for human health, many human diseases (including atheroscelerosis, cancer and arthritis) are caused or aggravated by an overzealous immune response. A greater understanding of what activates the immune response is therefore crucial for the design of novel therapies to treat these inflammatory disorders.
“Our study found that immune cells must first become ‘activated’ by eating a dying neighbouring cell before they are able to respond to wounds or infection. In this way, immune cells build a molecular memory of this meal, which shapes their inflammatory behaviour.”
>> Read the Full Article

For years, one of the major arguments that has been made against genetically engineered crops is the fear that, by tampering with a plant’s DNA, it could potentially cause health issues for consumers. It’s an understandable worry, however, the scientific consensus now seems to be undeniable: Whatever faults GMO crops may have, they are safe for human consumption.
>> Read the Full Article
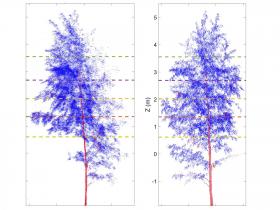
Most living organisms adapt their behavior to the rhythm of day and night. Plants are no exception: flowers open in the morning, some tree leaves close during the night. Researchers have been studying the day and night cycle in plants for a long time: Linnaeus observed that flowers in a dark cellar continued to open and close, and Darwin recorded the overnight movement of plant leaves and stalks and called it "sleep". But even to this day, such studies have only been done with small plants grown in pots, and nobody knew whether trees sleep as well. Now, a team of researchers from Austria, Finland and Hungary measured the sleep movement of fully grown trees using a time series of laser scanning point clouds consisting of millions of points each.
>> Read the Full Article
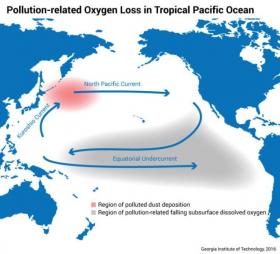
As climatologists closely monitor the impact of human activity on the world's oceans, researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology have found yet another worrying trend impacting the health of the Pacific Ocean.
A new modeling study conducted by researchers in Georgia Tech's School of Earth and Atmospheric Sciences shows that for decades, air pollution drifting from East Asia out over the world's largest ocean has kicked off a chain reaction that contributed to oxygen levels falling in tropical waters thousands of miles away.
"There's a growing awareness that oxygen levels in the ocean may be changing over time," said Taka Ito, an associate professor at Georgia Tech. "One reason for that is the warming environment -- warm water holds less gas. But in the tropical Pacific, the oxygen level has been falling at a much faster rate than the temperature change can explain."
The study, which was published May 16 in Nature Geoscience, was sponsored by the National Science Foundation, a Georgia Power Faculty Scholar Chair and a Cullen-Peck Faculty Fellowship.
In the report, the researchers describe how air pollution from industrial activities had raised levels of iron and nitrogen -- key nutrients for marine life -- in the ocean off the coast of East Asia. Ocean currents then carried the nutrients to tropical regions, where they were consumed by photosynthesizing phytoplankton.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment