
Put a tray of water in the freezer. For a while, it’s liquid. And then—boom—the molecules stack into little hexagons, and you’ve got ice. Pour supercold liquid nitrogen onto a wafer of yttrium barium copper oxide, and suddenly electricity flows through the compound with less resistance than beer down a college student’s throat. You’ve got a superconductor.
>> Read the Full Article

A very long time ago in a faraway galaxy, a star blew up. When the flash of light finally reached Earth on October 6, 2013, nobody noticed. Not at first. Three hours of supernova photons streamed by before an old telescope perched on a mountain north of San Diego started snapping pics.
>> Read the Full Article
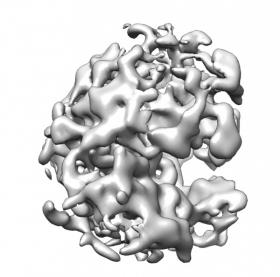
Research from York University’s Lassonde School of Engineering, has found a new set of algorithms that can help determine the 3D structure of proteins to one day find new treatments for a range of diseases including Alzheimer’s, HIV and cancer. The research, published in the current edition of the journal Nature Methods, shows that these new algorithms rapidly generate 3-D structures of viruses, which could revolutionize the development of new drug therapies.
>> Read the Full Article

By many accounts, winter seemed to stay mostly offstage in January. Rain was the star event, with warmer temperatures in the East having played a supporting role. Except for California: Parts of the Golden State saw more than 15 feet of snow, while mountain areas of the interior West, such as Colorado, Nevada and Utah, experienced higher-than-normal snowfall overall.
>> Read the Full Article

A new international study has demonstrated that deep-sea nodule mining will cause long-lasting damage to deep-sea life. This study, led by scientists at the National Oceanography Centre (NOC), was the first to review all the available information on the impacts of small-scale sea-floor disturbances simulating mining activity. It found clear impacts on marine ecosystems from deep-sea nodule mining activities, which lasted at least for decades.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment