
On July 22, 1847, a scouting party from The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints stood above the Great Salt Lake Valley in modern-day Utah; by 1870, more than 18,000 followers had colonized the valley and surrounding region, displacing Native American populations to establish dispersed farming communities. While historians continue to debate the drivers of this colonization event, a new study from the University of Utah proposes that agricultural productivity drove dispersal patterns in a process that led the current distribution of Utah populations today.
>> Read the Full Article

Flu shot season is here. But as you head to the doctor’s office or pharmacy to get vaccinated, scientists are working to make this yearly ritual a thing of the past. Researchers around the world, including at the University of Rochester Medical Center (URMC), are pursuing a “universal” flu vaccine, one that would protect against most or all seasonal and pandemic strains of the flu virus.
>> Read the Full Article

The ESA (European Space Agency) and NASA mission SOHO — short for Solar and Heliospheric Observatory — got a visit from an old friend this week when comet 96P entered its field of view on Oct. 25, 2017. The comet entered the lower right corner of SOHO’s view, and skirted up and around the right edge before leaving on Oct. 30. SOHO also spotted comet 96P in 1996, 2002, 2007 and 2012, making it the spacecraft’s most frequent cometary visitor.
>> Read the Full Article
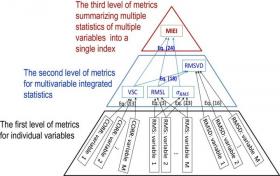
Many climate-related studies, such as detection and attribution of historical climate change, projections of future climate and environments, and adaptation to future climate change, heavily rely on the performance of climate models. Concisely summarizing and evaluating model performance becomes increasingly important for climate model intercomparison and application, especially when more and more climate models participate in international model intercomparison projects.
>> Read the Full Article

Cities around the globe are fueling evolution among microbes, plants, and animals, driving physical mutations and altering gene flow, according to a new analysis in the journal Science. The projected spread of urbanization in coming decades will continue to reshape and create new species in unexpected ways, the study found.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment