
Sediment found at the site of one of the largest lakes in Earth’s history could provide a fascinating new insight into how inland regions responded to global climate change millions of years ago.
A pioneering new study, carried out by a team of British-based researchers, has analysed sediments from the site of the vast lake which formed in the Sichuan Basin, in China, around 183 million years ago in the Jurassic period.
>> Read the Full Article

Rainfall patterns in the Sahara during the 6,000-year "Green Sahara" period have been pinpointed by analyzing marine sediments, according to new research led by a UA geoscientist.
What is now the Sahara Desert was the home to hunter-gatherers who made their living off the animals and plants that lived in the region's savannahs and wooded grasslands 5,000 to 11,000 years ago.
>> Read the Full Article

Lugano, Switzerland – Biosimilars create opportunities for sustainable cancer care, says the European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) in a position paper published in ESMO Open. The document outlines approval standards for biosimilars, how to safely introduce them into the clinic, and the potential benefits for patients and healthcare systems.
>> Read the Full Article

The U.S. now has two coal-burning power plants that avoid dumping carbon dioxide into the air. Petra Nova in Texas and Kemper in Mississippi use technology to stop CO2 in the smokestack and before combustion, respectively. Unfortunately, that makes two out of more than 400 coal-fired power plants in the U.S., the rest of which collectively pour 1.4 billion metric tons of the colorless, odorless greenhouse gas into the atmosphere each year. Even Kemper and Petra Nova do not capture all of the CO2 from the coal they burn, and the captured CO2 is used to scour more oil out of the ground, which is then burned, adding yet more CO2 to the atmosphere. The carbon conundrum grows more complex — and dangerous — with each passing year.
>> Read the Full Article

Over the past few years, a large fracture has grown across a large floating ice shelf on the Antarctic Peninsula. The world is watching the ice shelf, now poised to break off an iceberg the size of Delaware into the ocean.
It’s not a new phenomenon; this “thumb” of Antarctica, which juts out into the stormy Southern Ocean, has lost more than 28,000 square kilometers of floating ice — almost as large as Massachusetts — over the past half-century. This has included the complete disintegration of four ice shelves, the floating extensions of glaciers.
>> Read the Full Article

During periods of greater Atlantic hurricane activity, a protective barrier of vertical wind shear and cooler ocean temperatures forms along the U.S. East Coast, weakening storms as they approach land, according to a new study by NCEI scientist, Jim Kossin. In his paper, “Hurricane Intensification along United States Coast Suppressed during Active Hurricane Periods (link is external),” published in Nature, Kossin identifies this “buffer zone” and describes its relationship with both active and inactive periods of Atlantic hurricane activity.
>> Read the Full Article
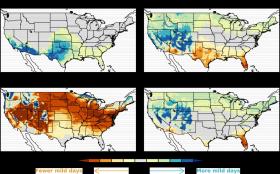
As scientists work to predict how climate change may affect hurricanes, droughts, floods, blizzards and other severe weather, there's one area that's been overlooked: mild weather. But no more.
NOAA and Princeton University scientists have produced the first global analysis of how climate change may affect the frequency and location of mild weather - days that are perfect for an outdoor wedding, baseball, fishing, boating, hiking or a picnic. Scientists defined "mild" weather as temperatures between 64 and 86 degrees F, with less than a half inch of rain and dew points below 68 degrees F, indicative of low humidity.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment