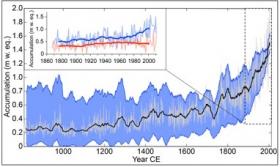
Snowfall on a major summit in North America’s highest mountain range has more than doubled since the beginning of the Industrial Age, according to a study from Dartmouth College, the University of Maine, and the University of New Hampshire.
articles
Polluted woods: leaves contaminate soil with hydrocarbon
In the Autumn leaves fall and apparently contaminate soil. It happens in the Italian woods where remediation is required by law for heavy hydrocarbon concentration greater than 50 milligrams per kilo.
La Tierra tuvo el 3er año más cálido hasta la fecha y el 5 ° más cálido registrado en noviembre
Con un comienzo cálido en el año y con sólo un mes para que termine, este 2017 sigue siendo el tercer año más cálido del globo terráqueo en el récord climático de 138 años.
Healthier Air due to the Low Emission Zone
The Low Emission Zone in Leipzig was established in March 2011, allowing only access of Diesel vehicles of Euro4 and higher with few exceptions. The ban of older vehicles and subsequent modernization of the car fleet resulted in slightly reduced PM10 and PM2.5 mass concentrations. However, the mass concentration of black carbon (soot particles) emitted mainly from Diesel vehicles decreased by 60% at the street site. These particles are believed to be most dangerous due to their carcinogenic trace compounds such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Furthermore, also the number concentration of ultrafine particles, which can penetrate deep into the lungs, decreased by approximately 70%. Despite modernized Diesel vehicles, nitrogen oxides concentrations did not follow these trends and remained nearly constant. The main achievement of the Low Emission Zone was the improvement of air quality by the reduction of the most dangerous particles.
Remote imaging advances medical diagnoses
University of Saskatchewan researcher Scott Adams has proven that MELODY telerobotic sonography, a French-developed system that allows doctors to do long distance ultrasound imaging, is feasible for abdominal and prenatal imaging. Adams is part of the first research team to test this technology in North America.
“The new telerobotic system could help save time and money. Patients may get earlier diagnoses while reducing the strain on major referral hospitals,” said U of S medical imaging professor Paul Babyn, Adams’s supervisor along with surgery professor Ivar Mendez.
Siting Solar, Sparing Prime Agricultural Lands
Unconventional spaces could be put to use generating renewable energy while sparing lands that could be better used to grow food, sequester carbon and protect wildlife and watersheds, says a study led by the University of California, Davis.