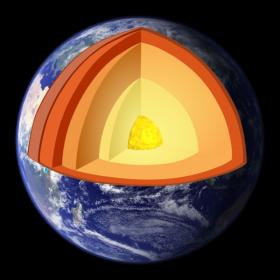
Researchers in Japan say they may be one step closer to solving the mystery at the core of the Earth.
articles
Substance in crude oil harms fish hearts, could affect humans as well
Research from Stanford University’s Hopkins Marine Station has identified a substance in oil that’s to blame for the cardiotoxicity seen in fish exposed to crude oil spills. More than a hazard for marine life exposed to oil, the contaminant this team identified is abundant in air pollution and could pose a global threat to human health.
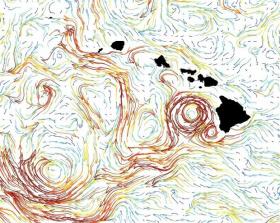
New ocean observations improve understanding of motion
Oceanographers commonly calculate large scale surface ocean circulation from satellite sea level information using a concept called “geostrophy,” which describes the relationship between oceanic surface flows and sea level gradient. Conversely, researchers rely on data from in-water current meters to measure smaller scale motion. New research led by University of HawaiÊ»i at MÄnoa oceanographer Bo Qiu has determined from observational data the length scale at which using sea level height no longer offers a reliable calculation of circulation.
Colorado's wildfire-stricken forests showing limited recovery
Colorado forests stricken by wildfire are not regenerating as well as expected and may partially transform into grasslands and shrublands in coming decades, according to a new University of Colorado Boulder study.
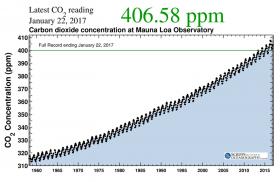
How the World Passed a Carbon Threshold and Why It Matters
Last year will go down in history as the year when the planet’s atmosphere broke a startling record: 400 parts per million of carbon dioxide. The last time the planet’s air was so rich in CO2 was millions of years ago, back before early predecessors to humans were likely wielding stone tools; the world was a few degrees hotter back then, and melted ice put sea levels tens of meters higher.
“We’re in a new era,” says Ralph Keeling, director of the Scripps Institution of Oceanography’s CO2 Program in San Diego. “And it’s going fast. We’re going to touch up against 410 pretty soon.”
How Stressful Will a Trip to Mars Be on the Human Body?
We Now Have a Peek Into What the NASA Twins Study Will Reveal