Tropical Cyclone Enawo was battering the northeastern region of Madagascar when NASA-NOAA's Suomi NPP satellite passed overhead on March 7. Enawo strengthened to the equivalent of a Category 4 or major hurricane and made landfall.
articles
Future climate change will affect plants and soil differently
A new European study has found that soil carbon loss is more sensitive to climate change compared to carbon taken up by plants. In drier regions, soil carbon loss decreased but in wetter regions soil carbon loss increased. This could result in a positive feedback to the atmosphere leading to an additional increase of atmospheric CO2 levels.
New Research Shows Crude Oil Chemicals Move and Change More Quickly than EPA Standards
The Environmental Protection Agency, or EPA, lists about 65 chemicals as “toxic pollutants” under the Clean Water Act, 16 of which are polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, or PAHs. LSU Department of Environmental Sciences doctoral candidate Parichehr Saranjampour conducted research on a chemical class of PAHs that is not on the EPA’s list — Dibenzothiophene, or DBT. DBT and its three related chemical compounds contain sulfur that is found in crude oil. Saranjampour studied how these chemical compounds move and change over time, which revealed new information that has never been published before. Her findings differ from the EPA’s information about these chemical compounds. This new research was published today in the Journal of Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry.
High number of deaths from heart disease, stroke and diabetes linked to diet
WHAT: Nearly half of all deaths in the United States in 2012 that were caused by cardiometabolic diseases, including heart disease, stroke and type 2 diabetes, have been linked to substandard eating habits, according to a study published in the March 7 issue of JAMA and funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI), part of the National Institutes of Health.
"Black swan" events strike animal populations
Black swan events are rare and surprising occurrences that happen without notice and often wreak havoc on society. The metaphor has been used to describe banking collapses, devastating earthquakes and other major surprises in financial, social and natural systems.
A new analysis by the University of Washington and Simon Fraser University is the first to document that black swan events also occur in animal populations and usually manifest as massive, unexpected die-offs. The results were published online March 7 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
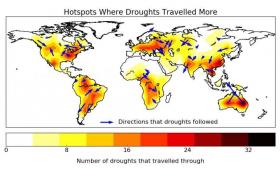
Traveling droughts bring new possibilities for prediction
A small subset of the most intense droughts move across continents in predictable patterns, according a new study published in the journal Geophysical Research Letters by researchers in Austria and the United States. The study could help improve projections of future drought, allowing for more effective planning.