Iron-rich meltwater from Greenland’s glaciers are helping fuel a summer bloom of phytoplankton.
articles
Changes in brain regions may explain why some prefer order and certainty, UCLA behavioral neuroscientists report
Why do some people prefer stable, predictable lives while others prefer frequent changes? Why do some people make rational decisions and others, impulsive and reckless ones? UCLA behavioral neuroscientists have identified changes in two brain regions that may hold answers to these questions.
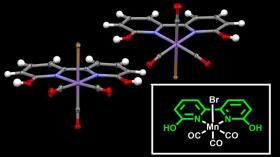
Recruiting Manganese to Upgrade Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is known as a greenhouse gas and plays an essential role in climate change; it is no wonder scientists have been looking for solutions to prevent its release in the environment. However, as a cheap, readily available and non-toxic carbon source, in the past few years there have been efforts to turn carbon dioxide into valuable wares, or ‘value-added’ products.
Sucking Up Spilt Oil
Spilt crude oil has repeatedly polluted and even destroyed marine ecosystems. An effective measure would be to remove spilt oil slicks by absorption into a separable solid phase. As Indian scientists now report in the journal Angewandte Chemie, congelation of the oil to a rigid gel within impregnated cellulose and scooping the particles out is possible.
Simple test predicts return of bladder cancer
Scientists have devised a simple test for an earlier and more accurate warning of returning bladder cancer than existing methods, according to research(link is external) published in the British Journal of Cancer(link is external).
QUT develops golden bananas high in pro-vitamin A
The decade-long research, led by Distinguished Professor James Dale, involved extensive laboratory tests at QUT as well as field trials in north Queensland.