To the vexation of school children and elation for their parents, residents living along the I-95 corridor of the northeastern United States know that El Niño in the Pacific will result in a dryer, warmer, and less snowy winter throughout the Appalachian, as certain as the adage ‘April showers bring May flowers.’ Such meteorological patterns where interannual variability in ocean temperatures affects climate have been long established in the field.
articles
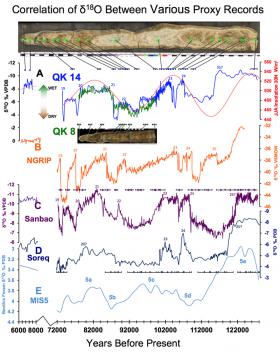
Stalagmites from Iranian Cave Foretell Grim Future for Middle East Climate
New study showed relief from current dry spell unlikely within next 10,000 years
Prelude to global extinction: Stanford biologists say disappearance of species tells only part of the story of human impact on Earth's animals
No bells tolled when the last Catarina pupfish on Earth died. Newspapers didn’t carry the story when the Christmas Island pipistrelle vanished forever.
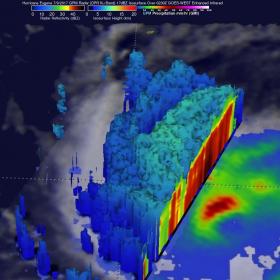
NASA Found Heavy Rainfall in Hurricane Eugene
When Hurricane Eugene was nearing its peak, NASA analyzed the storm's heavy rainfall over the open waters of the Eastern Pacific Ocean. That rainfall has lessened as Eugene has weakened to a tropical storm on July 11.
Hurricane Eugene formed on July 7, 2017, in the eastern Pacific Ocean south of the Baja Peninsula. On July 8 at 10:36 p.m. EDT (July 9 at 0236 UTC) the Global Precipitation Measurement mission or GPM core satellite passed over the storm and measured rainfall intensity.
Type 1 diabetes risk linked to intestinal viruses
Doctors can’t predict who will develop Type 1 diabetes, a chronic autoimmune disease in which one’s own immune system destroys the cells needed to control blood-sugar levels, requiring daily insulin injections and continual monitoring.
Warm winter events in the arctic are becoming more frequent, lasting longer
Arctic winter warming events – winter days when temperatures peak above minus 10 degrees Celsius – are a normal part of the Arctic climate over the ice-covered Arctic Ocean, but new research finds they are becoming more frequent and lasting longer than they did three decades ago.
A new study analyzing winter air temperatures over the Arctic Ocean from 1893 to 2017 shows that since 1980, an additional six Arctic winter warming events are occurring each winter at the North Pole and these events are lasting about 12 hours longer, on average. In December 2015, scientists recorded a temperature of 2.2 degrees Celsius (36 degrees Fahrenheit) in the Central Arctic, the warmest temperature ever recorded in this region from December through March.