Vastly expanding sugarcane production in Brazil for conversion to ethanol could reduce current global carbon dioxide emissions by as much as 5.6 percent, researchers report in the journal Nature Climate Change.
articles
Sea Level Rise Could Flood 1.9 Million U.S. Homes by 2100
An estimated 1.9 million U.S. homes could be flooded by 2100 if seas rise 6 feet in response to climate change, according to a new analysis by the real estate company Zillow. The affected properties are valued at $916 billion dollars and represent 1.8 percent of the country’s housing stock.
New Peruvian Bird Species Discovered By Its Song
A new species of bird from the heart of Peru remained undetected for years until researchers identified it by its unique song.
Zebra chip pathogen found in Western Canada for the first time
For the first time, evidence of the zebra chip pathogen has been found in potato fields in southern Alberta, but the University of Lethbridge’s Dr. Dan Johnson cautions against panic.
“So far, the zebra chip pathogen has appeared in only small numbers of potato psyllids,” says Johnson, a biogeography professor and coordinator of the Canadian Potato Psyllid and Zebra Chip Monitoring Network. “The number of potato psyllids in all Alberta sites is very low and many sample cards have found no evidence of the potato psyllid insect. Zebra chip does not normally become a problem unless the potato psyllids are found in much higher numbers than are currently being found in Canada.”
Rising Sea Levels Creating First Native American Climate Refugees
Rising sea levels and human activities are fast creating a "worst case scenario" for Native Americans of the Mississippi Delta who stand to lose not just their homes, but their irreplaceable heritage, to climate change.
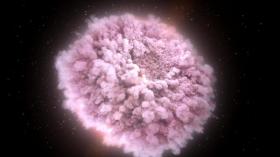
When stars collide
Wrap your mind around this: Neutron stars, the collapsed cores of once-large stars, are thought to be so dense that a teaspoon of one would weigh more than Mount Everest.
These are the kind of amazing astrophysical features that help fuel the research interests of Professor John Bally of the Department of Astrophysical and Planetary Sciences, who studies the formation of stars and planets (including luminous, transient objects in space).