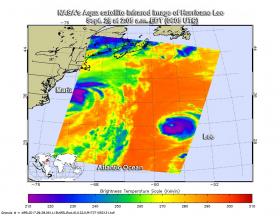
Hurricane Lee began weakening as NASA's Aqua satellite passed overhead and collected temperature information. Satellite data showed that Lee's strongest side was south of its center.
articles
NASA Glenn Tests Thruster Bound for Metal World
As NASA looks to explore deeper into our solar system, one of the key areas of interest is studying worlds that can help researchers better understand our solar system and the universe around us. One of the next destinations in this knowledge-gathering campaign is a rare world called Psyche, located in the asteroid belt.
Disease Resistance Successfully Spread from Modified to Wild Mosquitoes
Using genetically modified (GM) mosquitoes to reduce or prevent the spread of infectious diseases is a new but rapidly expanding field of investigation. Among the challenges researchers face is ensuring that GM mosquitoes can compete and mate with their wild counterparts so the desired modification is preserved and spread in the wild population. Investigators at Johns Hopkins University have engineered GM mosquitoes to have an altered microbiota that suppresses human malaria-causing parasites. These GM mosquitos preferred to mate with wild mosquitoes and passed along the desired protection to many generations of offspring.
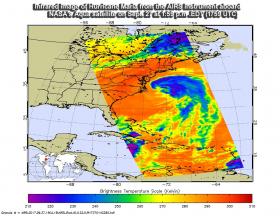
NASA Sees Maria Weaken to a Tropical Storm
NASA and NOAA satellites provided information and imagery to forecasters that showed Hurricane Maria weakened to a tropical storm on Sept. 28.
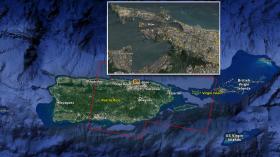
NASA Damage Map Aids Puerto Rico Hurricane Response
A NASA-produced map showing areas of eastern Puerto Rico that were likely damaged by Hurricane Maria has been provided to responding agencies, including the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA). The hurricane, a Category 4 storm at landfall on Puerto Rico on Sept. 20, caused widespread damage and numerous casualties on the Caribbean island, an unincorporated U.S. territory with a population of about 3.4 million.
DOE Should Take Steps Toward Facilitating Energy Development on Its Public Lands
The U.S. Department of Energy should place a higher priority on developing an accurate and actionable inventory of agency-owned or managed properties that can be leased or sold for energy development, says a new report from the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. The report recommends a sequence of activities DOE can follow to manage its lands and identify properties that have promising profiles for energy resource development.