
While cars powered by hydrogen fuel cells offer clear advantages over the electric vehicles that are growing in popularity (including their longer range, their lower overall environmental impact, and the fact that they can be refueled in minutes, versus hours of charging time), they have yet to take off with consumers. One reason is the high cost and complexity of producing, distributing, and storing the pure hydrogen needed to power them, which has hindered the roll-out of hydrogen refueling stations.
>> Read the Full Article

A study published Aug. 28, 2017, in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciencesadds a new dimension to the controversial decision to inject large amounts of chemical dispersants immediately above the crippled oil well at the seafloor during the Deepwater Horizon disaster in 2010. The dispersants likely reduced the amount of harmful gases in the air at the sea surface—diminishing health risks for emergency responders and allowing them to keep working to stop the uncontrolled spill and clean up the spilled oil sooner.
>> Read the Full Article

Chesapeake Bay, the largest estuary in the United States and one of the largest in the world, is facing new risks from a layer of highly acidified water some 10 to 15 meters below the surface, a new study has found.
This “pH minimum zone” is 10 times more acidic than the bay’s surface waters and may pose a risk to a variety of economically and ecologically important marine species, including oysters, crabs and fish, the researchers say. A decline in the number of calcium carbonate-shelled organisms – particularly oysters – may be hampering the bay’s ability to deal with the increase in acidity, they add.
>> Read the Full Article

No single solution exists for alleviating crowding in emergency rooms, but a new study identifies four key strategies that have reduced the problem.
The study, published in the journal Annals of Emergency Medicine, concludes that engaged executive leadership can alleviate the problem when combined with a data-driven approach and coordination across the hospital from housekeepers to the CEO. Crowding in emergency rooms has been associated with decreased patient satisfaction and even death.
>> Read the Full Article

When ethanol prices at the pump rise for whatever reason, it becomes economically advantageous for drivers of dual-fuel vehicles to fill up with gasoline. However, the health of the entire population pays a high price: substitution of gasoline for ethanol leads to a 30% increase in the atmospheric concentration of ultrafine particulate matter, which consists of particles with a diameter of less than 50 nanometers (nm).
>> Read the Full Article
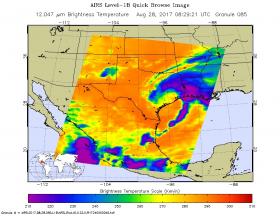
On Monday, Aug. 28 at 7 a.m. CDT the National Hurricane Center said the center of Harvey is emerging into the Gulf of Mexico. A NASA animation of imagery from NOAA's GOES East satellite shows Harvey as it lingered over southeastern Texas over the weekend of Aug. 26 and 27 and moving back toward the Gulf of Mexico on Aug. 28.
The National Hurricane Center noted "life-threatening flooding continues over southeastern Texas." NHC stressed that people should never attempt to travel into flooded roadways.
>> Read the Full Article

The full damage wreaked by Hurricane Harvey won’t be totaled up for days if not weeks, but thankfully the destruction so far has resulted in relatively few fatalities. The impact on energy infrastructure, though, is a different story. The storm hit southeast Texas, a major hub of the U.S. petroleum and natural gas industries. It stands as further evidence that the centralized model for fuel production and transportation is out-of-date, leaving the U.S. exposed to economic disruption and threats to national security. In the age of climate change, a more nimble and flexible approach is needed.
>> Read the Full Article

On Friday, August 25, U.S. Coast Guard Cutter Healy will sail from Dutch Harbor, Alaska, with a team of NOAA scientists and collaborators on a 22-day cruise to study environmental change in the western Arctic Ocean.
Scientists will track ecosystem responses to rapidly changing environmental conditions such as sea ice decline, ocean acidification and rising air and water temperature, as the ship travels north through the Bering, Chukchi and Beaufort seas.
>> Read the Full Article

Storm-tide sensors are being installed at key locations along the Texas Gulf Coast by the U.S. Geological Survey in advance of Hurricane Harvey.
Storm surge, coastal erosion and inland flooding are among the most dangerous natural hazards unleashed by hurricanes, with the capacity to destroy homes and businesses, wipe out roads, bridges, water and sewer systems, and profoundly alter landscapes. The USGS has experts on these hazards, state-of-the-science computer models for forecasting them, and sophisticated equipment for monitoring actual flood and tide conditions.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment