
As a young Marine stationed in South Carolina in 1981, Frank Roberts recognized that the state’s low country was ideal for oyster farming. His family harvested oysters in the Chesapeake Bay and Long Island Sound, and he had a hunch it would work in South Carolina too.
Roberts eventually started his own oyster farm in South Carolina — making a key contribution to a growing nationwide aquaculture trend worth $1.3 billion (2014 figure), with some help from NOAA.
>> Read the Full Article
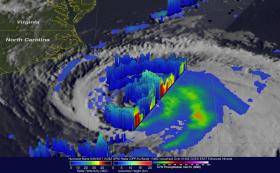
NASA’s Aqua satellite and Global Precipitation Measurement mission, or GPM, satellites have been peering into what appears to be a somewhat lop-sided Hurricane Maria. The storm appears asymmetric because vertical wind shear is pushing clouds and showers to the eastern side of the storm.
On Sept. 27, NHC forecaster Daniel Brown noted, “Deep convection and banding has increased over the eastern and northeastern portion of the large circulation of Maria since yesterday.”
>> Read the Full Article

One June day in the year 793, men in ships landed on Lindisfarne, an island off eastern England occupied by a monastery. The men, apparently from the north, plundered treasures, overthrew altars and set fire to buildings. They killed some monks and carried others off in chains; others, they stripped naked and left behind to the mercies of the weather. The attack shocked European Christian society. They came to mark it as the official start of the Viking Age, when Norse raiders ranged as far as the southern Mediterranean and northern Asia, before seemingly fading out some 250 years later.
>> Read the Full Article

The majority of people who are touched by an epileptic seizure event can only endure the terrifying moments and put their faith in doctors to help their loved one. The University of Lethbridge’s Dr. Artur Luczak, however, was in a position to do much more when his infant son suffered a seizure, and what he’s learned about seizures since has flipped the script on understanding how the brain functions during these traumatic events.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment