
York biology Professor Sapna Sharma is interested in predicting the effects of environmental stressors – for example, climate change, invasive species, land use change and habitat alteration − on ecosystems, and improving the scientific approaches used to generate these predictions. Some of her latest research, funded by the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) and others, and published in Scientific Reports, suggests that environmental stressors are driving the long-term changes in ice seasonality.
>> Read the Full Article
Cholera cases in East Africa increase by roughly 50,000 during El Niño, the cyclical weather occurrence that profoundly changes global weather patterns, new Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health research suggests.
The findings, researchers say, could help health ministries anticipate future cholera surges during El Niño years and save lives.
>> Read the Full Article
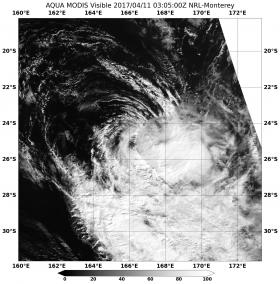
NASA's Aqua satellite observed how strong wind shear was literally pushing Tropical Cyclone Cook apart as it displaced the bulk of clouds to the southeast of the center.
NASA's Aqua satellite passed over Cook on April 11 at 0305 UTC (11:05 p.m. EST) and captured a visible and infrared image of the storm. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument took a visible image of the storm. The image showed that strong vertical wind shear had pushed the bulk of clouds and thunderstorms southeast of the center of circulation.
>> Read the Full Article

Global warming will thaw about 20% more permafrost than previously thought, scientists have warned; potentially releasing significant amounts of greenhouse gases into the Earth’s atmosphere.
A new international research study, including climate change experts from the University of Leeds, University of Exeter and the Met Office, reveals that permafrost is more sensitive to the effects of global warming than previously thought.
>> Read the Full Article

With spring finally here and warmer temperatures just around the corner, snow will slowly melt away, releasing us from the clutches of winter. However, that’s not the only thing that the melting snow will release. Researchers from McGill University and École de technologie supérieure in Montreal have found that urban snow accumulates a toxic cocktail from car emissions - pollutants that are in turn unleashed into the environment as the weather warms up.
>> Read the Full Article

In the wake of 2015 Climate Paris Agreements to limit global temperature below 2°C above pre-industrial levels, many governmental and private stakeholders have advocated for the introduction of policies to mitigate climate change. This would affect directly only the fossil-fuel and utility sector, but it would also expose indirectly many other economic sectors, in particular the energy-intensive sectors. The financial system can be affected due to its exposure to firms in the form of equity shares, bonds holdings and loans. However, the impact of climate policies on the financial system has remained unclear so far.
>> Read the Full Article
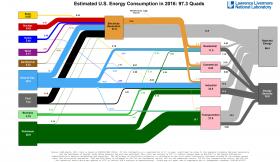
Americans used more renewable energy in 2016 compared to the previous year, according to the most recent energy flow charts released by Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. Overall, energy consumption was nearly flat.
Each year, the Laboratory releases energy flow charts that illustrate the nation's consumption and use of energy. Americans used 0.1 quads (quadrillion BTU), more in 2016 than in 2015. A BTU, or British Thermal Unit, is a unit of measurement for energy; 3,400 BTUs is equivalent to about 1 kilowatt-hour.
>> Read the Full Article

For the second time in just 12 months, scientists have recorded severe coral bleaching across huge tracts of the Great Barrier Reef after completing aerial surveys along its entire length. In 2016, bleaching was most severe in the northern third of the Reef, while one year on, the middle third has experienced the most intense coral bleaching.
>> Read the Full Article

One way to understand how ocean acidity can change, for example, in response to rising carbon dioxide (CO2) levels, is to look to the history of seawater acidity. Dr. Itay Halevy of the Weizmann Institute of Science has looked to the distant past – all the way back to Earth’s earliest oceans. The model he developed, together with Dr. Aviv Bachan of Stanford University, suggests that the early oceans, right around the time that life originated, were somewhat acidic, and that they gradually became alkaline. The study, published in Science, sheds light on how past ocean acid levels were controlled by CO2in the atmosphere, an important process for understanding the effects of climate change.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment