
What is "space weather"? And how might it affect weather on Earth?
Researchers have discovered a formerly undetected impact of space weather on the polar atmosphere, which may explain some previously unexplained variations in winter weather patterns. Their results, published today (Tuesday 14 October), in the journal Nature Communications could have important implications for seasonal weather forecasting.
>> Read the Full Article

A parasite spread by cat poop is causing a big problem for endangered sea otters in California, and researchers have finally figured out how. Sea otters were nearly wiped out by the fur trade at one point, but they've been slowly making a comeback thanks to conservation efforts and protection under the Endangered Species Act. While they're on the road to recovery the latest numbers from the U.S. Geological Survey released last month shows they're population growth has stalled, with the biggest issue being that they're dying in record numbers.
>> Read the Full Article
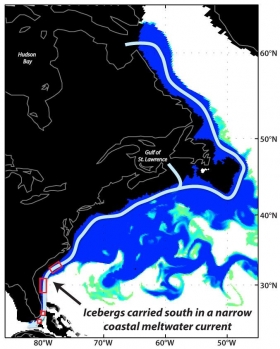
Using a first-of-its-kind, high-resolution numerical model to describe ocean circulation during the last ice age about 21,000 year ago, oceanographer Alan Condron of the University of Massachusetts Amherst has shown that icebergs and meltwater from the North American ice sheet would have regularly reached South Carolina and even southern Florida. The models are supported by the discovery of iceberg scour marks on the sea floor along the entire continental shelf.
Such a view of past meltwater and iceberg movement implies that the mechanisms of abrupt climate change are more complex than previously thought, Condron says. "Our study is the first to show that when the large ice sheet over North America known as the Laurentide ice sheet began to melt, icebergs calved into the sea around Hudson Bay and would have periodically drifted along the east coast of the United States as far south as Miami and the Bahamas in the Caribbean, a distance of more than 3,100 miles, about 5,000 kilometers."
>> Read the Full Article
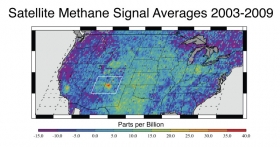
An unexpectedly high amount of the climate-changing gas methane, the main component of natural gas, is escaping from the Four Corners region in the U.S. Southwest, according to a new study by the University of Michigan and NASA.
The researchers mapped satellite data to uncover the nation's largest methane signal seen from space. They measured levels of the gas emitted from all sources, and found more than half a teragram per year coming from the area where Arizona, New Mexico, Colorado and Utah meet. That's about as much methane as the entire coal, oil, and gas industries of the United Kingdom give off each year.
>> Read the Full Article

With a busy week behind you and the weekend within reach, there's no shame in taking things a bit easy on Friday afternoon. With this in mind, every Friday TriplePundit will give you a fun, easy read on a topic you care about. So, take a break from those endless email threads, and spend five minutes catching up on the latest trends in sustainability and business.
>> Read the Full Article

Ecosystems in the Middle East are home to a wealth of unique species – including the ancestors of many of our staple crops today. Yet the climate scenario in this dry region is alarming. Already, the region has a relatively small amount of water available for every person living there – and it is predicted that in the future, there will be even less rain. That could jeopardize Middle Eastern ecosystems and threaten the survival of important species.
>> Read the Full Article

An unexpectedly high amount of the climate-changing gas methane, the main component of natural gas, is escaping from the Four Corners region in the US Southwest, according to a new study by the University of Michigan and NASA. The researchers mapped satellite data to uncover the nation's largest methane signal seen from space. They measured levels of the gas emitted from all sources, and found more than half a teragram per year coming from the area where Arizona, New Mexico, Colorado and Utah meet. That's about as much methane as the entire coal, oil, and gas industries of the United Kingdom give off each year.
>> Read the Full Article

Poland says it will need cash and help in curbing its emissions if it is to sign up for a new decade of EU green energy policy at talks this month, according to a document seen by Reuters.
The document shows the 28 EU member states are broadly ready to agree a new set of 2030 goals to follow on from 2020 energy and environment policy, although Europe's biggest power Germany says it will not agree a deal "at any price".
>> Read the Full Article

Open pipes, widely used for a variety of purposes across the western U.S. landscape, have been reported as a "potentially very large" source of bird mortality according toresearch by scientists at Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL). The finding was part of a peer-reviewed study accepted for publication by the "Western North American Naturalist" and authored by Charles D. Hathcock and Jeanne M. Fair.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment