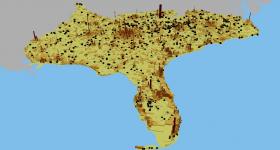
New mapping methods developed by researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory can help urban planners minimize the environmental impacts of cities’ water and energy demands on surrounding stream ecologies.
In an analysis published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, an ORNL-led team used high-resolution geospatial modeling to quantify the effects of land, energy, and water infrastructures on the nation’s rivers and streams.
>> Read the Full Article
A fast, simple blood test for ulcerative colitis using infrared spectroscopy could provide a cheaper, less invasive alternative for screening compared to colonoscopy, which is now the predominant test, according to a study between the Department of Physics and Astronomy and the Institute for Biomedical Sciences at Georgia State University.
>> Read the Full Article

In recent decades, change has defined our environment in the United States. Agriculture intensified. Urban areas sprawled. The climate warmed. Intense rainstorms became more common. But, says a new University of Wisconsin–Madison study, while those kinds of changes usually result in poor water quality, lakes have surprisingly stayed the same.
>> Read the Full Article

Infection with human papilloma virus (HPV) is the primary cause of cervical cancer and a subset of head and neck cancers worldwide. A University of Colorado Cancer Center paper describes a fascinating mechanism that links these two conditions – viral infection and cancer. The link, basically, is a family of enzymes called APOBEC3. These APOBEC3 enzymes are an essential piece of the immune system’s response to viral infection, attacking viral DNA to cause disabling mutations. Unfortunately, as the paper shows, especially the action of family member APOBEC3A can spill over from its attack against viruses to induce DNA mutations and damage in the host genome as well. In other words, this facet of the immune system designed to scramble viral DNA can scramble human DNA as well, sometimes in ways that cause cancer.
>> Read the Full Article

Arthritis is the most-widespread joint disease, with around 90 percent of all people over 65 being affected to varying degrees, but this degenerative disease is also widespread amongst younger people. In arthritis, the cartilage in the joint, a type of protective layer on bones that "lubricates" the joint, degenerates over time. This can be extremely painful for sufferers, because inflammatory reactions are associated with cartilage degeneration. In the later stages of the disease, bones are no longer adequately protected and can directly rub against each other.
Arthritis can affect all joints in the body, but most often affects the knee joint, hip joint and fingers. The disease has been considered incurable until now. Current treatment methods, such as anti-inflammatory drugs and painkillers, mainly address the symptoms. Often, the only remaining option is an operation to replace the affected joint with an artificial one.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment