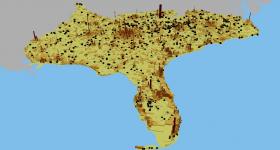
New mapping methods developed by researchers at the Department of Energy’s Oak Ridge National Laboratory can help urban planners minimize the environmental impacts of cities’ water and energy demands on surrounding stream ecologies.
In an analysis published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, an ORNL-led team used high-resolution geospatial modeling to quantify the effects of land, energy, and water infrastructures on the nation’s rivers and streams.