For coral reefs, the threat of climate change and bleaching are bad enough. An international research group led by Cornell University has found that plastic trash – ubiquitous throughout the world’s oceans – intensifies disease for coral, adding to reef peril, according to a new study in the journal Science, Jan. 26.
articles
How To Save a Town From Rising Waters
The only land route that connects Isle de Jean Charles, Louisiana, to the rest of the continental United States is Island Road, a thin, four-mile stretch of pavement that lies inches above sea level and immediately drops off into open water on either side. Even on a calm day, salt water laps over the road’s tenuous boundaries and splashes the concrete.
Mosquitoes Remember Human Smells, But Also Swats, Virginia Tech Researchers Find
Your grandmother’s insistence that you receive more bug bites because you’re ‘sweeter’ may not be that far-fetched after all, according to pioneering research from Virginia Tech scientists.
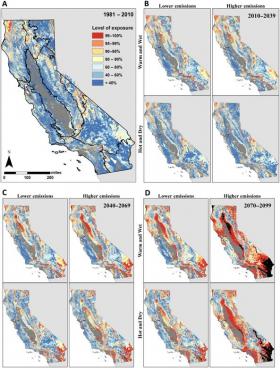
Nearly Half of California's Vegetation at Risk From Climate Stress
Current levels of greenhouse gas emissions are putting nearly half of California’s natural vegetation at risk from climate stress, with transformative implications for the state’s landscape and the people and animals that depend on it, according to a study led by the University of California, Davis. However, cutting emissions so that global temperatures increase by no more than 2 degrees Celsius (3.2 degrees Fahrenheit) could reduce those impacts by half, with about a quarter of the state’s natural vegetation affected.
Repurposed Drug Found to be Effective Against Zika Virus
In both cell cultures and mouse models, a drug used to treat Hepatitis C effectively protected and rescued neural cells infected by the Zika virus — and blocked transmission of the virus to mouse fetuses.
Phosphorus Pollution Reaching Dangerous Levels Worldwide, New Study Finds
Man-made phosphorus pollution is reaching dangerously high levels in freshwater basins around the world, according to new research.