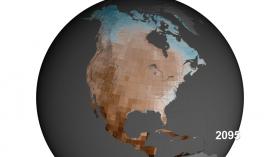
To help untangle fact from speculation, Cornell climate scientists and their colleagues have developed a “robust null hypothesis” to assess the odds of a megadrought – one that lasts more than 30 years – occurring in the western and southwestern United States. The research was published online Dec. 8 in the Journal of Climate.
articles
Marine Turtles Dying After Becoming Entangled in Plastic Rubbish
Hundreds of marine turtles die every year after becoming entangled in rubbish in the oceans and on beaches, including plastic ‘six pack’ holders and discarded fishing gear.
Southern Africa's Cheetah Population Much Smaller Than Believed
Populations of cheetahs in southern Africa have declined as farming and other human activities push deeper into the free-roaming cats’ range, a new study co-led by Duke University doctoral student Varsha Vijay finds.
Native Fish Species at Risk Following Water Removal from the Colorado River
Agriculture and domestic activities consume much of the Colorado River water that once flowed to the Colorado Delta and Northern Gulf of California. The nature and extent of impact of this fresh-water loss on the ecology and fisheries of the Colorado Delta and Gulf of California is controversial. A recent publication in the journal PeerJ reveals a previously unseen risk to the unique local biodiversity of the tidal portion of the Delta.
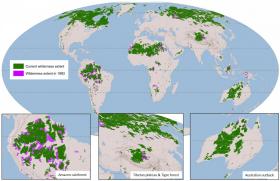
New Maps Show Shrinking Wilderness Being Ignored At Our Peril
Maps of the world’s most important wilderness areas are now freely available online following a University of Queensland and Wildlife Conservation Society-led study published today.
Shatter-Proof Mobile Phone Screens a Step Closer With ANU Research
An international study on glass led by ANU and the Institut de Physique du Globe de Paris in France could lead to the development of shatter-proof mobile phone screens.