
China met its 2020 carbon intensity target — the amount of carbon dioxide it produces per unit of economic growth — three years ahead of schedule, according to the country’s top climate official, Xie Zhenhua. In 2017, China cut its carbon intensity by 46 percent from 2005 levels, a drop of 5.1 percent from the previous year, the state-run Xinhua News Agency reported.
Xie announced the milestone at the country’s Green Carbon Summit on Monday.
>> Read the Full Article

As many of Hawaiʻi‘s leading water professionals near retirement, there’s an urgent need to train a new local workforce of scientists. That’s happening at the University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa thanks to ʻIke Wai, a large five-year project funded by the National Science Foundation that aims to understand how water moves and is captured and stored underground in Hawaiʻi. Its main study sites include the Kona and Pearl Harbor aquifer systems.
>> Read the Full Article
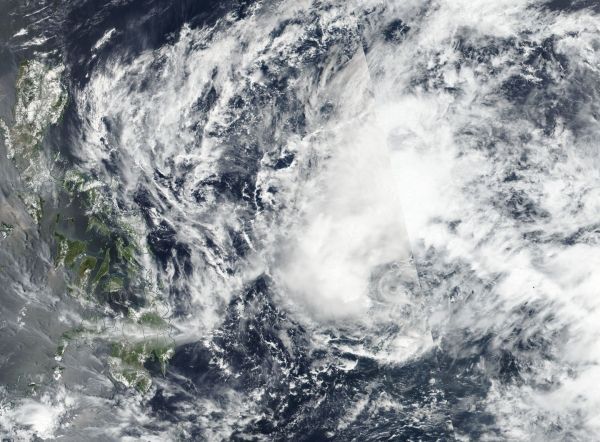

Satellite imagery showed that Tropical Depression Jelawat was still dealing with southerly vertical wind shear that was pushing the bulk of its clouds north of its center.
On March 27, Jelawat was centered over 100 miles from Yap State in the Northwestern Pacific Ocean. Yap State is one of four states in the Federated States of Micronesia. The other states are Chuuk State, Kosrae State and Pohnpei State.
>> Read the Full Article
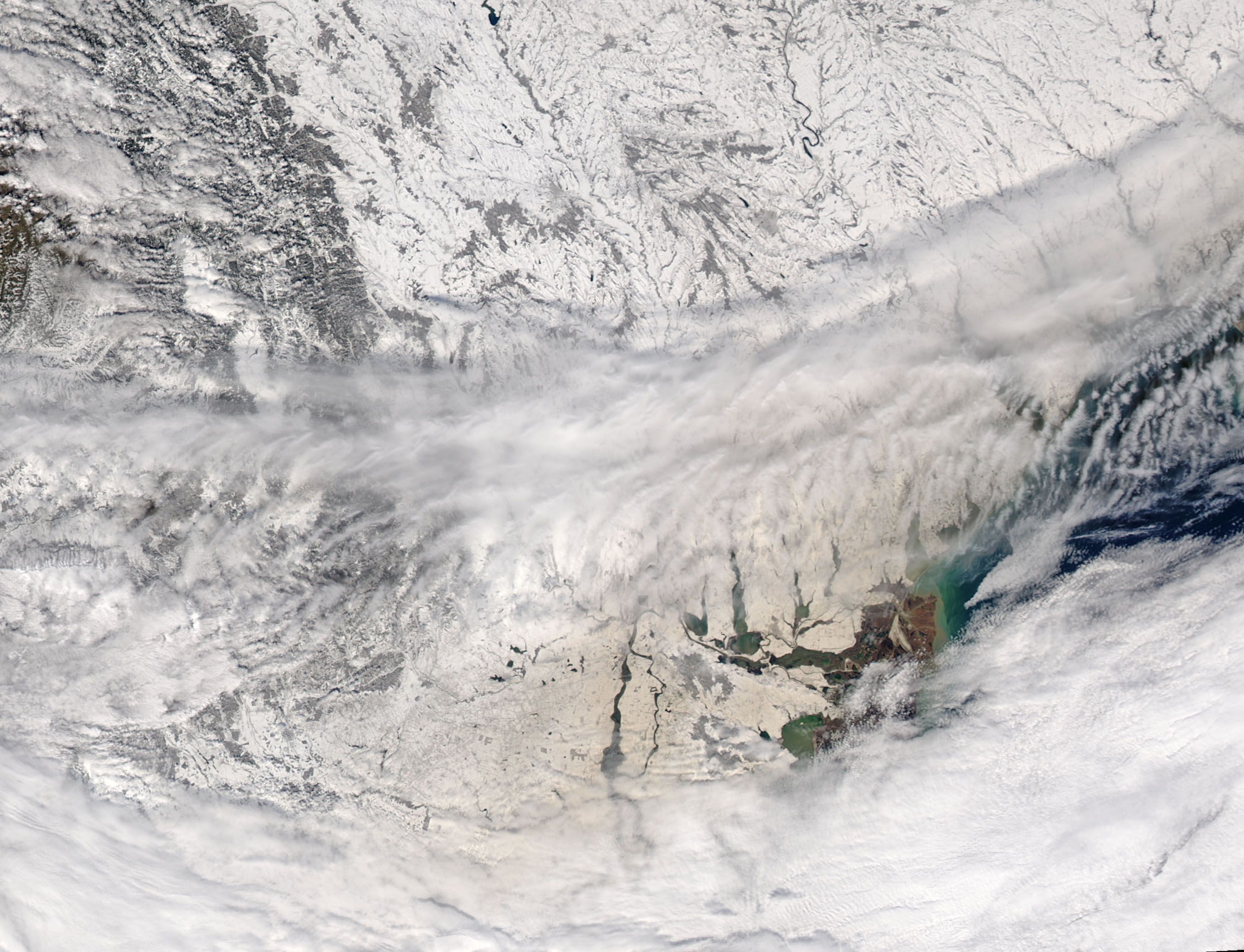
Maybe this is what it would be like to ski on Mars.
In late March 2018, the people of Eastern Europe and Russia found their snow cover had a distinctly orange tint. The color came from vast quantities of Saharan dust that was picked up by strong winds, lofted over the Mediterranean Sea, and deposited on Bulgaria, Romania, Moldova, Ukraine, and Russia. Skiers in the Caucasus Mountains snapped photos that looked like they could have come from the Red Planet.
>> Read the Full Article
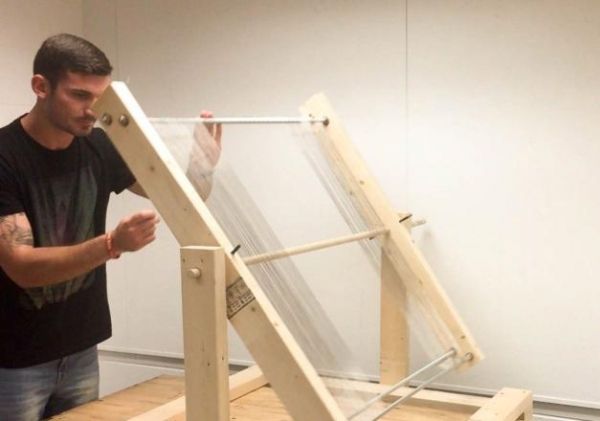

Fog harvesting may look like whimsical work.
After all, installing giant nets along hillsides and mountaintops to catch water out of thin air sounds more like folly than science. However, the practice has become an important avenue to clean water for many who live in arid and semi-arid climates around the world.
>> Read the Full Article

According to researchers at Aalto University, Finland, large-scale weather cycles, such as the one related to the El Niño phenomenon, affect two-thirds of the world’s cropland. In these so called climate oscillations, air pressure, sea level temperature or other similar factors fluctuate regularly in areas far apart in a way that causes rain and temperature patterns to shift significantly.
>> Read the Full Article
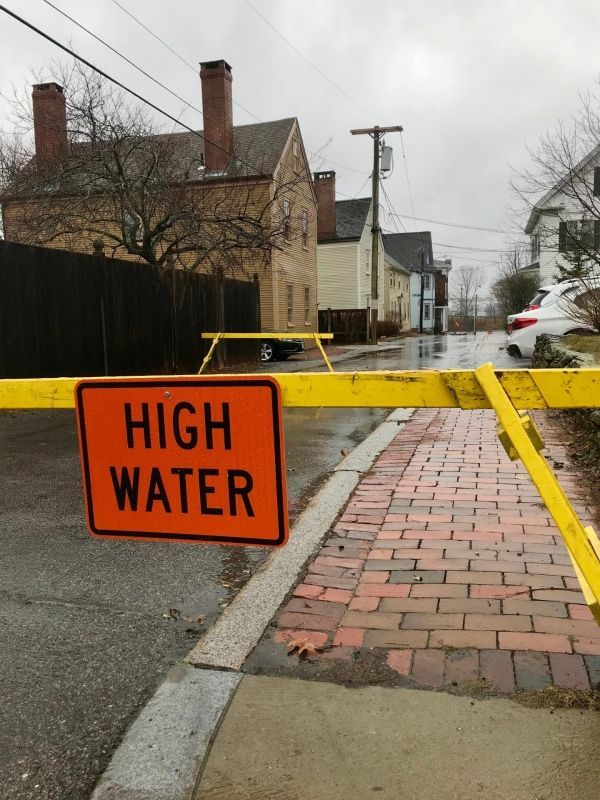

High tide floods, or so-called “nuisance flooding,” that happen along shore roadways during seasonal high tides or minor wind events are occurring far more frequently than ever before. Researchers at the University of New Hampshire have found that in the past 20 years roads along the East Coast have experienced a 90 percent increase in flooding – often making the roads in these communities impassable, causing delays, as well as stress, and impacting transportation of goods and services.
>> Read the Full Article

 ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment
ENN
Environmental News Network -- Know Your Environment